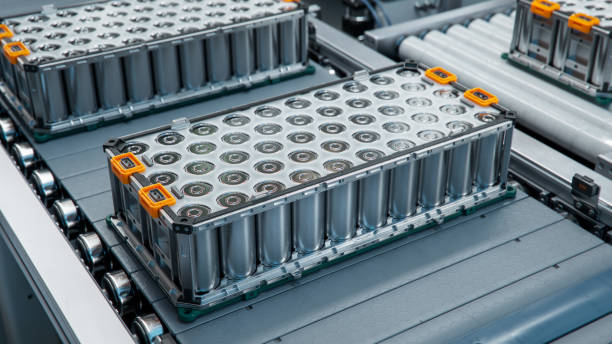
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become a focal point of the automotive industry’s transition toward a more sustainable future. The heart of every EV lies in its battery, a component that significantly impacts the vehicle’s performance, range, and overall efficiency. With advancements in technology, numerous battery types have emerged, each offering unique benefits and challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the different EV battery types, their pros and cons, and future innovations that could revolutionize the electric vehicle market.
Understanding Electric Vehicle Batteries
At the core of EV innovation is the electric vehicle battery, designed to store energy that powers the vehicle’s electric motor. While there are different types of batteries used in electric vehicles, each type has its unique characteristics in terms of capacity, lifespan, charging speed, and cost. Let’s dive deeper into the most commonly used types.
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
The Backbone of Modern EVs
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most widely used type of battery in electric vehicles today. This battery type is known for its high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively light weight, which makes it the ideal choice for EV manufacturers.
Pros of Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries provide more energy per unit weight, allowing for a longer driving range.
- Long Lifespan: These batteries typically last for 8 to 15 years, offering durability for EV owners.
- Faster Charging Times: They charge more quickly than other battery types, minimizing downtime.
- Lightweight: Li-ion batteries are lighter than many other types, contributing to better overall vehicle efficiency.
Cons of Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Cost: Despite recent reductions in cost, Li-ion batteries remain expensive, which increases the upfront price of EVs.
- Thermal Management Issues: Li-ion batteries can overheat under extreme conditions, requiring advanced cooling systems.
- Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of lithium-ion batteries have significant environmental concerns, particularly in terms of resource extraction and e-waste.
2. Solid-State Batteries
The Future of EV Batteries?
Solid-state batteries are often touted as the next breakthrough in battery technology for electric vehicles. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which promises to offer a safer and more efficient solution.
Pros of Solid-State Batteries:
- Increased Safety: Solid-state batteries are far less likely to catch fire or explode compared to their liquid-based counterparts.
- Higher Energy Density: They can store more energy in a smaller space, increasing the driving range of EVs.
- Longer Lifespan: Solid-state batteries are expected to last longer and offer more charge cycles than current lithium-ion batteries.
Cons of Solid-State Batteries:
- High Manufacturing Costs: The technology is still in its infancy, and scaling up production remains a challenge.
- Limited Availability: Solid-state batteries are not yet available in large quantities, and few EV manufacturers are currently using them.
- Temperature Sensitivity: They may be more sensitive to temperature extremes, impacting performance.
3. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
The Predecessor of Lithium-Ion Technology
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries were once the standard in electric vehicles, but have since been largely replaced by lithium-ion batteries. However, they are still used in some hybrid vehicles today.
Pros of NiMH Batteries:
- Safety: NiMH batteries are less prone to overheating and are more stable under various conditions.
- Longer Lifespan: These batteries have a good lifecycle, often lasting between 10 to 15 years.
- Eco-Friendly: The materials used in NiMH batteries are less harmful to the environment than those in lithium-ion batteries.
Cons of NiMH Batteries:
- Lower Energy Density: NiMH batteries offer a lower energy density compared to lithium-ion, resulting in a shorter range for EVs.
- Heavier: These batteries are generally heavier, affecting vehicle performance.
- Slower Charging: NiMH batteries take longer to charge compared to newer technologies.
4. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries
A Safer Alternative to Lithium-Ion
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) is a type of lithium-ion battery that uses iron phosphate as the cathode material. This technology is gaining popularity in various applications, including electric vehicles, due to its safety features and durability.
Pros of LiFePO4 Batteries:
- Safety: LiFePO4 batteries are more stable and less likely to overheat or catch fire.
- Longer Lifespan: These batteries typically offer more charge cycles than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Lower Cost: LiFePO4 batteries are cheaper to produce, reducing the overall cost of EVs.
Cons of LiFePO4 Batteries:
- Lower Energy Density: The energy density of LiFePO4 batteries is lower than traditional lithium-ion batteries, resulting in a reduced driving range.
- Performance in Cold Temperatures: LiFePO4 batteries are less efficient in cold weather, affecting performance and range.
5. Zinc-Air Batteries
A New Contender in EV Battery Technology
Zinc-air batteries, while still under development, show great promise as a potential alternative to lithium-based batteries. These batteries utilize zinc and oxygen from the air as their primary components.
Pros of Zinc-Air Batteries:
- High Energy Density: Zinc-air batteries can store more energy than most other battery types, offering potentially longer driving ranges.
- Eco-Friendly: Zinc is abundant and less harmful to the environment compared to other materials used in EV batteries.
- Lower Cost: Zinc is cheaper to source than lithium, making zinc-air batteries more affordable in the long run.
Cons of Zinc-Air Batteries:
- Limited Commercialization: Zinc-air batteries are still in the experimental stage and not yet commercially viable for large-scale EV production.
- Performance Issues: The technology still faces challenges in terms of power output and cycling stability.
Future Innovations in EV Battery Technology
The future of EV batteries is incredibly exciting, with several groundbreaking innovations on the horizon. Researchers are exploring a wide range of alternative materials and technologies to make batteries more efficient, safer, and cheaper.
1. Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are being explored as a potential replacement for lithium-ion batteries. Sodium is more abundant and cheaper than lithium, making these batteries a potentially more affordable option for mass-market EVs.
2. Graphene Batteries
Graphene is a material with remarkable electrical properties, and it could be the key to the next generation of EV batteries. Graphene batteries promise faster charging times, longer lifespans, and higher energy densities.
3. Wireless Charging
One of the most promising innovations in EV battery technology is wireless charging. With wireless charging, EVs could charge automatically as they are parked, eliminating the need for plugs and wires.
Conclusion
As electric vehicles become more mainstream, advancements in battery technology will play a crucial role in shaping their future. Each battery type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the key to success lies in finding the right balance of cost, performance, and sustainability. Whether it’s the tried-and-true lithium-ion, the emerging solid-state batteries, or future innovations like sodium-ion and graphene, EV battery technology is rapidly evolving. Understanding these technologies and their pros and cons will help consumers make informed decisions and drive the future of electric vehicles.