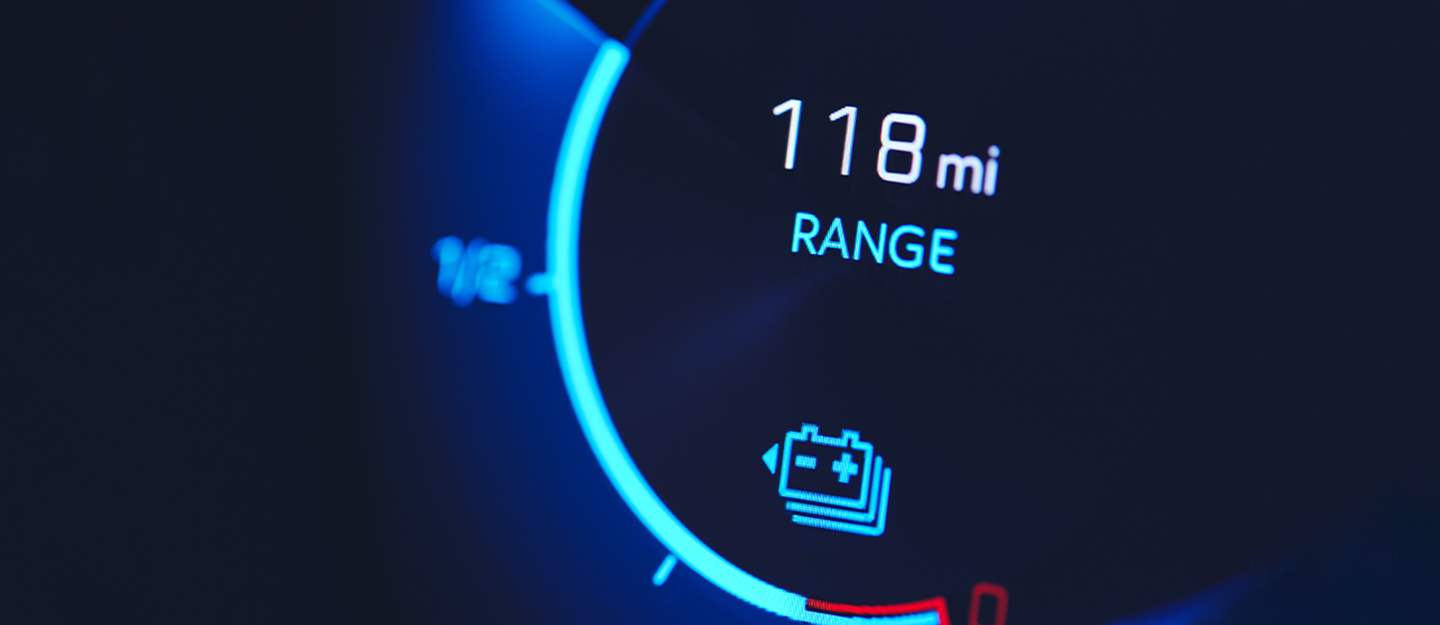
As the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) continues to rise, one of the biggest concerns for consumers remains range anxiety—the fear of running out of battery before reaching a charging station. EV range extenders provide a practical solution to this challenge, enhancing the driving range and efficiency of electric vehicles. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what EV range extenders are, how they work, and their impact on EV performance and sustainability.
What is an EV Range Extender?
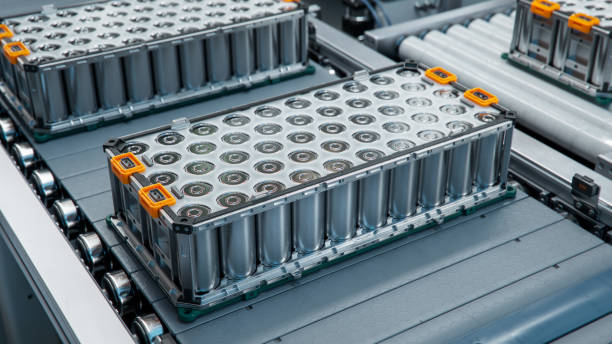
An EV range extender (REx) is a supplementary power source that extends the driving range of an electric vehicle. Typically, it is a small internal combustion engine (ICE) or an additional battery module designed to generate electricity and recharge the main battery while the vehicle is in motion. Unlike conventional hybrid vehicles, the range extender does not directly drive the wheels but acts as a backup power generator.
Types of EV Range Extenders
- Internal Combustion Engine-Based Range Extenders
- These use a small gasoline or diesel engine to generate electricity for the battery.
- Common in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
- Examples include the BMW i3 REx and Chevrolet Volt.
- Battery-Based Range Extenders
- Additional battery modules that provide extra power when the primary battery is depleted.
- Ideal for long-range EV models.
- Examples include Tesla’s battery swap technology.
- Fuel Cell Range Extenders
- Uses hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity.
- Environmentally friendly with zero emissions.
- Examples include Hydrogen-powered vehicles like the Toyota Mirai.
How EV Range Extenders Work
Step-by-Step Functionality
- Battery Depletion Detection: The system monitors battery levels and activates the range extender when the charge drops below a certain threshold.
- Electricity Generation: The range extender (engine, battery, or fuel cell) generates electricity, supplying power to the battery or directly to the motor.
- Continuous Driving: This process allows the vehicle to continue its journey without stopping for a recharge.
- Automatic Shutdown: Once the primary battery is sufficiently recharged, the extender shuts off to preserve fuel or energy.
Benefits of EV Range Extenders
1. Reduced Range Anxiety
- Eliminates the fear of running out of battery power on long journeys.
- Allows EV owners to travel greater distances with confidence.
2. Improved Efficiency
- Optimizes battery usage by supplementing power when needed.
- Reduces overall energy consumption, enhancing EV efficiency.
3. Enhanced Sustainability
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels in comparison to fully gasoline-powered cars.
- When using hydrogen or additional batteries, the system remains environmentally friendly.
4. Lower Charging Infrastructure Dependence
- Less reliance on EV charging stations, making long trips more convenient.
- Useful in areas with limited charging infrastructure.
5. Cost Savings on Battery Replacement
- Extends the lifespan of the primary battery by preventing complete depletion cycles.
- Reduces the need for frequent battery replacements, saving maintenance costs.
Challenges and Limitations of EV Range Extenders
1. Additional Weight and Space Consumption
- Extra components add weight and reduce cargo space.
- May affect the overall aerodynamics of the vehicle.
2. Higher Initial Cost
- Vehicles equipped with range extenders tend to have a higher upfront price.
- Increased maintenance costs if an internal combustion engine is used.
3. Emission Concerns for ICE-Based Extenders
- While more efficient than traditional engines, ICE-based range extenders still produce carbon emissions.
- Not a completely emission-free solution unless fuel-cell or battery-based extenders are used.
Popular EV Models with Range Extenders
- BMW i3 REx
- Uses a small two-cylinder gasoline engine to recharge the battery.
- Provides an additional 80-100 miles of range.
- Chevrolet Volt
- A plug-in hybrid with an engine that activates once the battery is depleted.
- Offers up to 420 miles of total range with a full tank and battery.
- Nissan e-Power Series Hybrid
- Uses a gasoline engine to generate electricity but does not drive the wheels.
- Popular in the Japanese market for its efficiency.
- Toyota Mirai (Fuel Cell Vehicle)
- Uses a hydrogen fuel cell to generate power.
- Zero emissions and longer range compared to traditional battery EVs.
Future of EV Range Extenders
The future of EV range extenders is rapidly evolving with advancements in battery technology, hydrogen fuel cells, and renewable energy sources. Automakers are investing in solutions that improve range and efficiency without compromising environmental sustainability.
Key Trends to Watch:
- Solid-State Batteries: Lighter, more efficient, and offering higher capacity.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A promising alternative to traditional gasoline-based range extenders.
- Solar-Powered Extenders: Some automakers are experimenting with solar panels to supplement battery charging.
- Ultra-Fast Charging Networks: Reduced need for range extenders with more widespread charging infrastructure.
Conclusion
EV range extenders are a game-changing technology that addresses range anxiety while enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles. Whether through gasoline generators, battery modules, or hydrogen fuel cells, these extenders offer a practical and sustainable way to improve the driving experience of EV owners. As advancements continue, range extenders will likely become smaller, more efficient, and environmentally friendly, paving the way for a smoother transition to fully electric mobility.